What is Conditional Logic? How does it work?
Engagement Strategies
5 Min Read
Discover how conditional logic enhances quizzes, forms, and workflows by personalizing experiences, boosting engagement, and improving efficiency.
Conditional logic is a powerful feature widely used in modern quiz builders, online form creators, and interactive survey tools to personalize user experiences. It allows you to display specific questions, results, or form fields based on a user’s previous responses. This smart content flow ensures each participant engages with content that is relevant and meaningful, significantly improving engagement, completion rates, and data quality.
At Quizify.io, conditional logic is central to building dynamic quizzes, forms, and surveys. Whether you’re building a quiz funnel for lead generation, gathering customer insights, or segmenting audiences, this feature streamlines the interaction and enhances the user journey.
How Conditional Logic Works?
To a large extent, conditional logic can be described as an “IF this, AND/OR/OR else that” approach. It involves processing user input to compare it with specific conditions predetermined to arrive at an ideal action to take. This enables you to control the direction that users take and possibly provide them with a more informed path through the site.
For instance, when taking an online quiz if a user clicks on a certain answer to a quiz question, the next question given can be related to the user's previous answer. In a form, some of the fields can be conditioned to appear or disappear depending on what has been filled out by the user.
How conditional logic operates:
Product Recommendations: If a customer selects electronics to be shown as the product of their category of interest then the subsequent steps as will be illustrated will show the products of that category. If they instead choose “Clothing” the recommended items will change to suit that category.
Quizzes & Surveys: Move questions in a sequence according to the answers provided earlier. It also avoids the problem of asking the wrong questions to users which will lead to users being more interested.
Forms: Some of the fields appear or disappear depending on the options the users will choose. For example, if a person chooses Yes to own a car, s/he might be asked the following questions related to his/her car’s model. If they choose “No” the car-related questions will not be displayed.
Workflows: Foster sophisticated functionality of follow-up emails depending on the users’ activity or split users into groups regarding their responses.
Types of Conditional Logic:
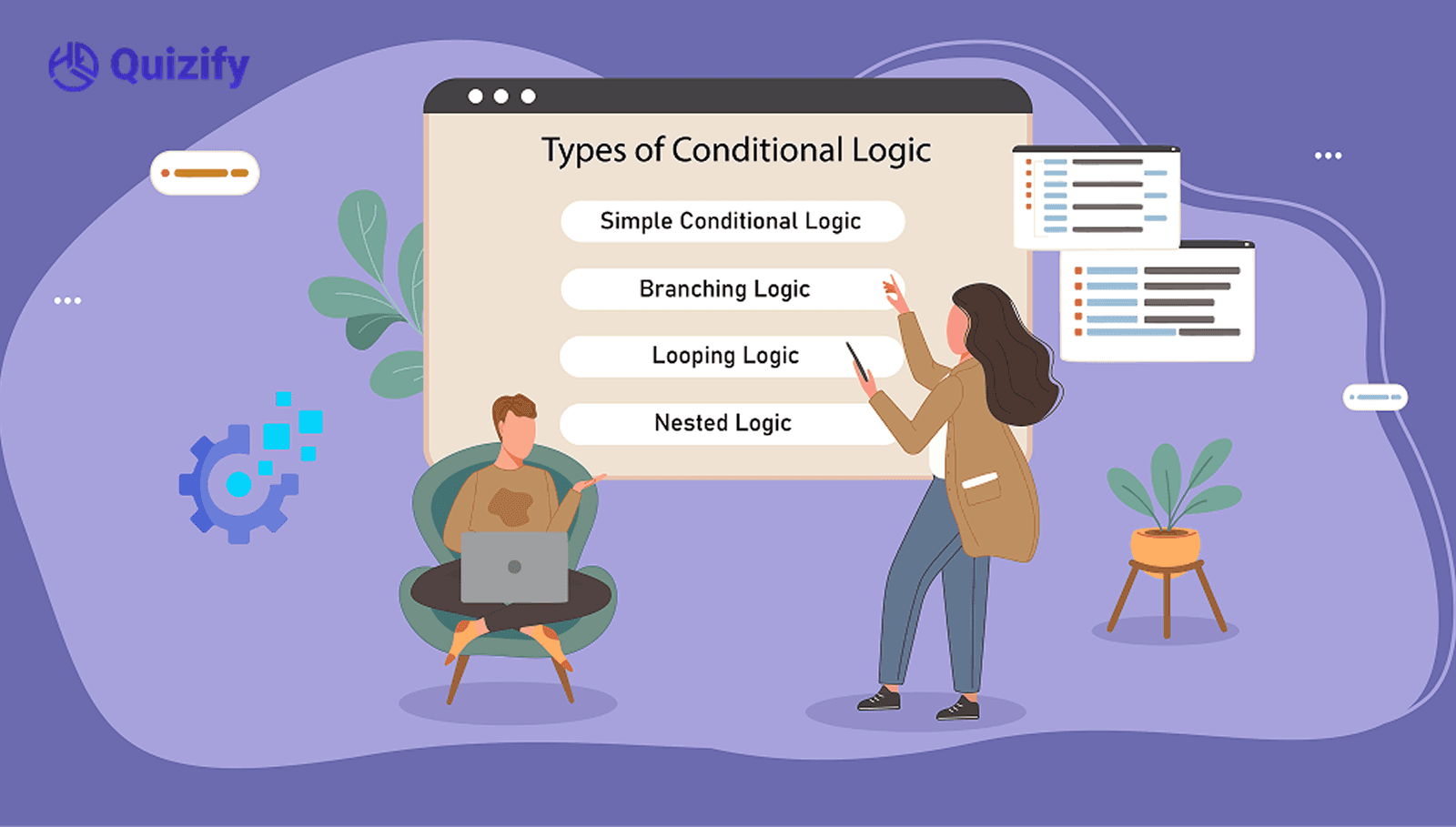
Several variations of conditional logic can be employed, depending on the complexity of the task:
Simple Conditional Logic: It will often be simple, black-and-white conditions, like showing one question or field if another is filled in by the user.
Branching Logic: Enables decision trees that contain more than one branch at a time, where upon completion of a set of conditions the user is directed to a specific branch. This is very much helpful in cases where there are long forms or quizzes and the results could go in a variety of ways.
Nested Logic: Figures within figures, meaning one can build even further on a set of conditions to achieve an even more favorable output. For example, if a user chooses a particular product type, they might find other subcategories. Additional filters could also be applied within a subcategory based on the user’s input of some value.
Looping Logic: This is used when several instructions require a response and the same condition is occasioned several times. It is helpful in fresh page entry situations such as in keeping track of inventory or in any situation that requires the user to enter several identical data sets into a program.
Benefits of Using Conditional Logic:
Personalization at Scale: Conditional logic is one of Sweet Chariots strong suits because it can be used to create unique experiences without any need for SMOs. Whether in quizzes, or forms of surveys, the user is fed content of solution suggestions that match their demeanor and treatment of brand contents.
Higher Engagement Rates: While using conditional logic it familiarizes users with substantial content because it offers materials by their activity. They do not receive countless unnecessary questions or fields, which makes the process more fun and less stressful. This, in turn, lowers the chances of drop-off rates in surveys, quizzes, or forms, among other things.
Efficiency and Automation: Conditional logic is beneficial for businesses because it reduces the workload and wastes less time. This can be done through the automation of the lead scoring, follow-up emails, segmentation of the users, and many more with less effort.
Actionable Insights: Conditional logic helps in getting more proper and constructive information from the respondents. It is more likely that users would give responses out of this initiative, and since the questions are properly guided, then such insights could drive the decision-making process.
Enhanced User Experience: Whenever it is a quiz, or customer support, enabling conditional logic helps in rendering functionalities much more efficient for the user at hand. Such a response makes users feel that the system is somehow responsive to their needs hence there is always improvement in user satisfaction and perception of the brand.
Increased Conversion Rates: When applied in form and customer journeys, conditional logic can increase conversion rates by a great percentage. With a few fields to fill in, and all those being necessary, the visitor is more likely to accomplish what is expected of him, whether it is to fill in a form, make a purchase, or sign up for a service or an account.
Application of Conditional Logic:

1. E-commerce Personalization:
Sometimes online stores have conditional logic for offering a unique buying experience. To be precise, based on certain patterns in the customer usage of products, the stores can recommend a particular product, modify the recommendations according to certain patterns, or offer suitable or attractive offers according to the taste of the customer.
2. Customer Support Workflows:
Conditional reasoning is applied most commonly to automate customer service. As a result, based on how customers respond to primary questions, they are directed to the proper section or given the correct information. This relieves the burden of system navigation on customers and designers and saves time for both customer support teams.
3. Lead Qualification:
Conditional logic, especially in marketing, is usually used in lead generation forms. When contacting and interacting with the leads, they are categorized according to the nature of their prospect’s reactions, after which they are followed up on through automation and sent to the relevant marketing EU section for communication, either an email series or direct sales communication.
4. Surveys and Market Research:
This makes the work of the question being asked have a logic to it which makes it reduces questions being seen by those who should not see them hence good work is done in statistical collection. This is especially applicable where a population consists of a very large number of individuals, and lengthy questionnaires with unnecessary questions demoralize participants and produce erroneous results.
5. Educational Quizzes:
Computer-based training or any online training that one can undertake employs conditional logic for the quizzes and tests to change as the learner progresses. This makes it possible to present the students with good questions that will test their knowledge as well as feedback on areas of strength and areas of emphasis.
Conclusion
Conditional logic is more than just a feature—it’s a strategic component that enhances every interaction within a quiz, survey, or online form. By leveraging it on platforms like Quizify.io, you can build smarter content that speaks directly to your audience, improves their experience, and drives real business results.
Whether you're creating a lead generation quiz, a product recommendation quiz, or an interactive survey, conditional logic ensures your users stay engaged—and your data stays actionable.
Join our newsletter list
Sign up to get the most recent blog articles in your email every week.
Similar Topic